Flow Rates
Flow rate is the volume of fluid that flows through a pipe or other enclosed region each second. Suppose we would want to describe the flow rate a fluid flows through a pipe:
- Mass flow rate – Mass of a substance which flows per unit of time, units kg/s
- Volumetric flow rate – Volume of a substance which flows per unit of time, units m3/s
The relationship that relates to the mass flow rate and the volumetric flow rate is the density:
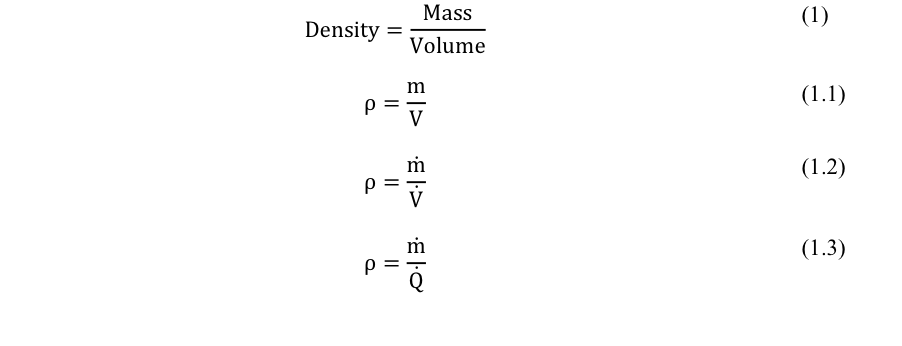
m˙ – Mass flow rate, Q – Volumetric flow rate
The units of density are kg/m3 which are derived from the standard density equation (1.1). Thus, having the units of time will cancel and the units of density will be the same.
Flow Rate Examples
- The mass flow rate of a fluid is 6 g/s with a density of 2 kg/cm3. What is the volumetric flow rate in m3/s?
- If a fluid is flowing through a cone-shaped pipe
a. what is the difference between the inlet and outlet mass flow rates? Show your workings.
b. If the density is constant will the volumetric flow rate be the same at the inlet and outlet? Show your workings.
Mean Velocity
If the size of the pipe is known and the flow rate is known we can find the mean velocity. Velocity is the rate of change of the position of an object with respect to a frame of reference and time and mean velocity is the average velocity of a fluid in motion.
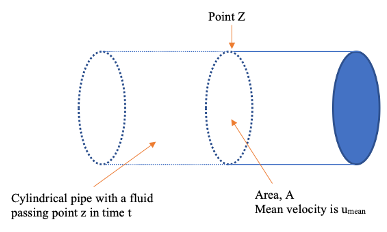
Figure 1: Cylindrical pipe with fluid flowing through
The area of the cross-section of the pipe at point z is A and at this point the mean velocity is umean. In a period fluid will pass point z with a length of umeant as (distance = speed x time).
Using the mean velocity, we can develop an expression for the volumetric flow rate:
 Using the previous equations (1.3 and 1.7), we express the mass flow rate using the mean velocity along a cylindrical pipe:
Using the previous equations (1.3 and 1.7), we express the mass flow rate using the mean velocity along a cylindrical pipe:
 Both expressions (1.7 and 1.8) are true for any shape of duct, as long as the condition of the cross-sectional area being perpendicular to the velocity is meet.
Both expressions (1.7 and 1.8) are true for any shape of duct, as long as the condition of the cross-sectional area being perpendicular to the velocity is meet.

Dr. Adam Zaidi, PhD, is a researcher at The University of Manchester (UK). His doctoral research focuses on reducing carbon dioxide emissions in hydrogen production processes. Adam’s expertise includes process scale-up and material development.’



