What Is a Valve?
A valve is a device that is used to either regulate, direct or control flow within a pipeline. It may be a mechanical operation but the function is very much required for chemical engineering operations. Based on the requirement, allowed pressure drop, and flow rate we can employ different kinds of valves.
Valves often change the flow pattern in pipelines. This may be due to the obstruction or restriction offered by the valve body. Here boundary layer separation may occur, which leads to the formation friction. In order to calculate form friction pertaining to that particular valve, we have L/D ratios and K values.
Common Types of Valves
Here are some of the most common valves using in industries such as pharmaceutical, wastewater treatment, oil & gas, food, and much more.
Control Valves
- Control valves are a special class of valves that are highly useful in controlling the flow of a fluid in pipelines from a control room.
- The control valve contains a stem that can be varied by giving the setpoints from the distributed control system(DCS), which are useful to a lot of processing operations.
Globe Valves
- Globe valves offer better control of the flow but at the expense of large pressure drop.
- One of the most used control valves.
- Generally used for regulating flows and pressures.
 Gate Valves
Gate Valves
- Gate valves use a gate to facilitates the flow of fluid. It will slide from completely open to a closed position. In gate valves, the sliding stem can be movable or fixed stationary.
- Generally used to completely shut off the fluid flow and once opened a full fluid flow is provided.
 Ball Valves
Ball Valves
- Ball valves contain a ball as a flow regulating element. The ball contains a provision to allow the flow. One quarter (1/4) turn of the valve handle can regulate the flow from minimum to maximum.
- Contains a spherical disc that rotates around a hollow center.
- Used for throttling gases and vapor.
- Mainly used for low flow conditions.
Plug Valves
- Plug valves are similar to a Ball valve but the regulating element will be different. A conical disc is used.
- Suitable for open and close applications.
- Can not be used for throttling as the velocity at which the fluid would pass through the valve would be far too high.
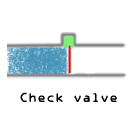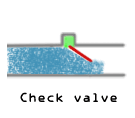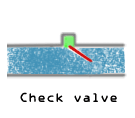
Check Valves (Non-Returning Valves)
- Check valves or non-returning valves allow flow only in one direction.
- This works with the use of pressure differential as the inlet side of the valve would require a higher pressure than the outlet side to open the valve.
- This is particularly useful in reactor inlets, where exothermic reactions might happen in pipelines.
 Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves
- Butterfly valves contain a disk that can rotate from 0 to 90 degrees for a complete close to open state. This valve can be used as a control valve in water service.
Diaphragm Valves
- Similar to the Globe valve, a diaphragm valve contains a plate-like arrangement that functions as a stem in the Globe valve.
- Diaphragm valves are very useful in changing the velocity of the fluid flow by regulating the area in which fluid can enter and exit the valve.
These are only a few of the many valves that are out of the industry and to this day new valves are being created to optimize the process of a unit. To name a few Solenoid valves, needle valves, etc.

Adrian graduated with a Masters Degree (1st Class Honours) in Chemical Engineering from Chester University along with Harris. His master’s research aimed to develop a standardadised clean water oxygenation transfer procedure to test bubble diffusers that are currently used in the wastewater industry commercial market. He has also undergone placments in both US and China primarely focused within the R&D department and is an associate member of the Institute of Chemical Engineers (IChemE).